AI in Cybersecurity Explained: Key Takeaways
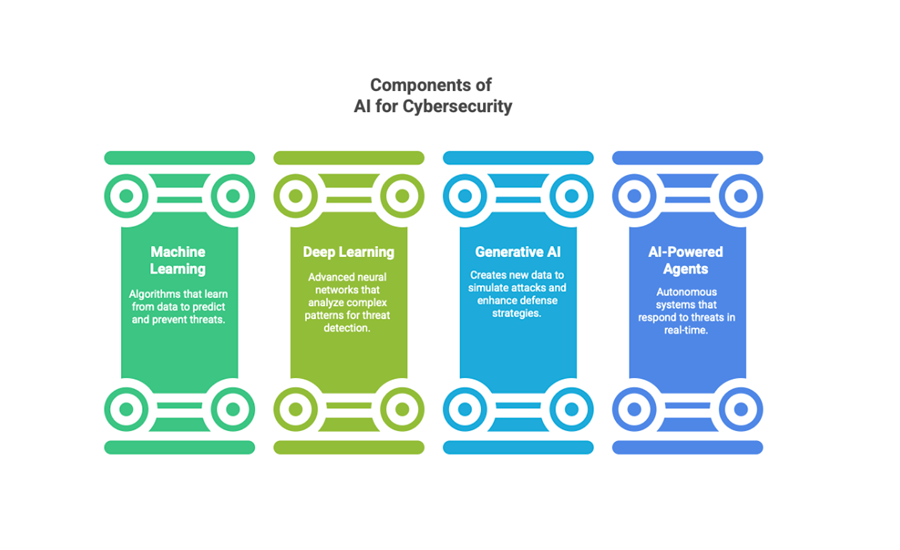
- The four components of AI for cybersecurity include machine learning, deep learning, generative AI, and AI-powered agents
- AI in cybersecurity can help detect threats faster and automate repetitive tasks
- While AI can triage alerts, detect anomalies, and generate reports, it still relies on analysts for context, decision-making, and oversight
With the market expected to hit $60.6 billion by 2028, it’s clear that organizations aren’t just curious, they’re investing.
And it makes sense, as it highlights how essential AI has become in defending against evolving cyberthreats.
If you’re looking to strengthen detection, reduce manual workload, or improve how your team handles alerts, AI tools are becoming a practical and worthwhile investment.
In this guide, we will help you:
- Break down the 4 core components of AI in cybersecurity
- Identify where AI adds value and where it falls short
- Explore how Forgepath’s AI-powered services can help you detect threats faster, cut down on alert fatigue, and scale your security operations
4 Components of AI for Cybersecurity
When it comes to AI in cybersecurity, these four components form the backbone of how it strengthens cybersecurity defenses.
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is one of the most practical and widely used applications of AI in cybersecurity.
By learning from past data and recognizing patterns enables systems to operate more independently. That means identifying trends, detecting threats, and responding faster without constant human oversight.
It allows systems to:
- Recognize unusual activity or behaviors that could indicate a breach
- Classify known and unknown threats in real time
- Continuously refine detection models based on new data
2. Deep Learning
Deep learning takes machine learning a step further by using multilayered neural networks, also known as models built to work like the human brain.
This makes it effective at making sense of complex data, like network traffic, endpoint activity, or user behavior patterns.
It’s used to:
- Dig through massive volumes of data from emails, endpoints, and cloud systems to spot potential risks
- Uncover hard-to-detect threats, like stealthy malware, zero-days, or advanced persistent attacks
- Help analysts find what others miss by revealing hidden patterns in network traffic
3. Generative AI
Generative AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond in plain, everyday language.
It can also create original content based on the data it’s been trained on, making it useful for everything from answering questions to generating reports.
Security teams are putting generative AI to work to make investigations faster and workflows more efficient.
It helps by:
- Allowing analysts to interact with tools using everyday language instead of code
- Automatically generating reports, summaries, and other documentation
- Offering smart, context-aware answers during incident response
4. AI-Powered Agents
Consider AI-powered agents as your virtual teammates. They work at scale and respond in real time, adapting to what’s happening across your environment.
By taking over repetitive, high-volume tasks, these agents free up your team to focus on more strategic work.
For instance, they can:
- Triage alerts from phishing attempts, insider threats, or data loss
- Adjust access controls based on real-time user behavior
- Spot and prioritize the vulnerabilities that need attention first
AI-Powered Cybersecurity Tools
AI enhances a wide range of cybersecurity tools, making them faster, smarter, and more adaptive.
1. Next-Generation Firewalls
Traditional firewalls follow static rules set by administrators to allow or block traffic.
Think of them as gatekeepers that only act on predefined instructions. If a threat doesn’t match a known rule, it might slip through unnoticed.
Next-generation firewalls build on that by using AI and live threat intelligence, giving them the ability to spot new and unknown threats (and make smarter decisions down the line).
2. AI-Driven Endpoint Protection
AI strengthens endpoint security by identifying vulnerabilities like outdated software or unusual behavior, such as unexpected data transfers or the presence of malware.
In active attack scenarios, it can automatically contain threats by isolating the affected endpoint from the rest of the network.
3. Intelligent Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDPS)
AI enhances intrusion detection and prevention systems by enabling faster, more accurate analysis of network traffic.
These systems can:
- Scan vast volumes of data
- Detect unauthorized access attempts
- Stop intrusions before they escalate
4. Cloud Security With AI Insight
With multicloud environments becoming the norm, tracking threats across platforms is a major challenge.
AI helps by analyzing data from across cloud apps, services, and infrastructures to identify misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and cross-cloud attack patterns.
5. Securing IoT Devices With AI
The rapid growth of connected devices expands the attack surface, making IoT a prime target for cyber threats.
AI helps by:
- Monitoring device behavior
- Flagging anomalies like unauthorized access or unusual traffic
- Detecting coordinated attacks across multiple endpoints
A 2024 study showed that CART-based machine learning detected IoT threats with 91–98% accuracy, highlighting AI’s ability to provide scalable protection in complex environments.
Top Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
Looking to get more out of your AI-powered security tools? These benefits make a strong case.
1. Faster Threat Detection
According to a 2023 AI in Cybersecurity Report, faster threat detection is one of the top benefits organizations gain from using AI.
That’s no surprise, as security tools like SIEM and XDR generate thousands of alerts every day.
Most are harmless, but missing the few that matter can have serious consequences, such as:
- Undetected breaches
- Delayed incident response
- Data exfiltration that goes unnoticed until it’s too late
Instead of getting buried in routine alerts, AI highlights the ones that truly require attention.
2. Smarter Reporting
Generative AI takes on the heavy lifting of reporting.
It pulls from multiple data sources and puts together summaries and reports that are easy to understand and share, saving analysts hours of manual effort.
3. Finding Hidden Vulnerabilities
AI helps uncover risks you might not know are there, like outdated systems, unknown devices, or unprotected sensitive data.
It gives you a more complete picture of what needs attention before attackers find those weak spots.
4. Helping Analysts Grow Faster
Generative AI makes it easier for newer team members to get up to speed.
They don’t need to write complex queries to run investigations, and they can lean on AI for step-by-step guidance and recommendations.
That means junior analysts can take on more advanced work sooner.
5. Delivering Actionable Insights You Can Trust
By pulling data from logs, network traffic, and threat feeds, AI can surface attack patterns and emerging risks that might otherwise go unnoticed.
It brings everything together to help your team make faster, more informed decisions.
6. Lowering Fewer False Positives (and Negatives)
Ever feel overwhelmed by a flood of alerts that lead nowhere? You’re not alone.
In fact, 43% of organizations say reducing false positives is a top reason they’re turning to AI, and it’s easy to see why.
With so many alerts, it’s hard to separate real threats from routine noise. AI can help by using techniques like behavior analysis and contextual correlation to filter out the distractions and surface the alerts that truly matter.
7. Scaling With Your Environment
As your environment gets more complex, AI doesn’t slow down.
It handles data-heavy workloads, evolves with new attack methods, and takes repetitive tasks off your team’s plate, so they can concentrate on higher-level threats.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Cybersecurity: Is AI a Threat?
As promising as AI is, putting it to work in cybersecurity isn’t always straightforward.
So, what makes AI in cybersecurity tough to implement?
1. Job Displacement Concerns
About 32% of U.S. workers believe AI could limit their future job prospects. And in cybersecurity, that concern is growing.
It’s natural to feel uneasy when AI starts taking over tasks you’ve done for years, but AI isn’t a substitute for human judgment.
Instead, it’s changing the role of security professionals, making upskilling and adaptability more important than ever.
2. High False Positive Rates and Analyst Overload
AI tools aren’t perfect, and they can sometimes mistake normal behavior for a threat, triggering false alarms.
And while these alerts still need a human to double-check them, too many false positives can quickly overwhelm analysts and lead to alert fatigue.
3. Infrastructure Demands and Skills Gaps
AI doesn’t run on autopilot. It still needs computing power, storage, and the right infrastructure to work effectively.
On top of that, building and maintaining AI models takes skilled people. And that kind of talent (and time) isn’t always easy to find, especially for smaller teams.
4. Data Privacy and Monitoring Risks
To spot threats, AI systems often track user behavior and look for anything out of the ordinary. It’s effective, but it also raises privacy concerns.
Constant monitoring across systems and networks can feel intrusive, and organizations need to balance security with respecting user privacy.

Explore Artificial Intelligence Security at Forgepath
While AI is a great tool for accelerating detection, automation, and decision-making, it’s not infallible.
They still require human validation, especially in sensitive environments, to avoid erroneous or risky automated actions that could impact security, compliance, or customer trust.
At Forgepath, our Artificial Intelligence Security services are built to reduce risk, build trust, and keep you compliant.
We deliver the full spectrum of AI security, from deep technical assessments to executive-level oversight, so you can scale safely, securely, and in control.
AI in Cybersecurity: FAQs
What is AI in cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, AI helps teams stay ahead of threats by spotting patterns in large amounts of data, automating detection, and responding to incidents in real time, often before a human could react.
AI works by observing behavior across your network to establish a baseline of normal activity.
The moment AI spots behavior that deviates from the norm, such as a policy violation or access attempt, it acts fast to flag or block the threat.
How is AI used in cybersecurity?
AI helps security teams detect threats faster, cut down on false positives, and automate repetitive tasks. It’s built into tools like endpoint protection, intrusion detection systems, and SIEM or XDR platforms.
These systems use AI to recognize patterns in large amounts of data and flag suspicious activity before it becomes a serious issue.
What are the biggest risks of using AI in cybersecurity?
Some of the main risks include false positives, privacy concerns, and a lack of transparency in how AI makes decisions.
There’s also the threat of attackers targeting the AI itself. On top of that, teams need the right infrastructure and skills to manage these tools properly.
Can AI fully replace human analysts in security operations?
No. While AI can definitely speed things up and take care of a lot of the repetitive tasks, it still needs people in the loop.
Security analysts play a key role in understanding the bigger picture, making tough calls, and handling complex situations that AI might miss.

![The ROI of Penetration Testing [Formula & FAQs]](https://forgepath.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/roi-penetration-testing-hero-image-768x469.jpg)